We’ve received requests to provide a flyer based on the online info graphic on EbolaFacts.com and you have it attached. This flyer can be distributed in places where internet access is poor. If you have the ability to make copies, please do so. If you know someone who may be able to print some copies, please forward this to them.
The flyer contains the information available on the website. We’ve delivered it in PDF format so most printers should be able to use it.
We have left a space on the back for you to add the name of your organization or logo or whatever other information you feel you need to add. We only ask that the information on the flyer remain untouched.
If you do decide to do this, please let us know as we would like to give you credit as a partner on our website. Thanks so much.
Ebola is deadly, but is preventable. Spread the message to save lives!
The Liberian government has recently instituted enhanced measures to combat the spread of Ebola, many of which will likely make travel to and from and within the country difficult. The government has taken the following steps:
- Closed all borders except major entry points (Roberts International Airport, James Spriggs Payne Airport, Foya Crossing, Bo Waterside Crossing, and Ganta Crossing).
- Instituted prevention and screening measures at entry points that remain open. This new travel policy will affect incoming and outgoing travelers.
- Instituted restrictions on public and other mass gatherings
- Instituted quarantine measures for communities heavily affected by Ebola; travel in and out of those communities will be restricted
What is Ebola?
Ebola virus disease is a rare and deadly disease. The disease is native to several African countries and is caused by infection with one of the ebolaviruses (Ebola, Sudan, Bundibugyo, or Taï Forest virus). It is spread by direct contact with a sick person’s blood or body fluids. It is also spread by contact with contaminated objects or infected animals.
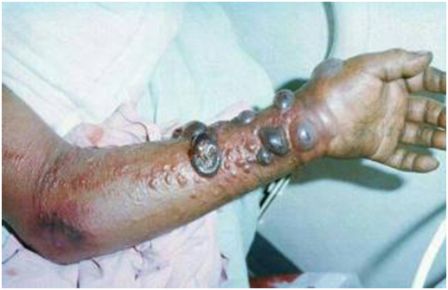
Symptoms include fever, headache, joint and muscle aches, sore throat, and weakness, followed by diarrhea, vomiting, and stomach pain. Skin rash, red eyes, and internal and external bleeding may be seen in some patients.
Who is at risk?
Cases of Ebola virus disease are seen sporadically throughout Africa. Travelers could be infected if they come into contact with blood or body fluids from someone who is sick or has died from Ebola, sick wildlife, or meat from an infected animal. Health care providers caring for Ebola patients and family and friends in close contact with an ill person are at highest risk because they may come into contact with blood or body fluids.
What can travelers do to prevent Ebola?
There is no vaccine for Ebola and no specific treatment. It is important to take steps to prevent Ebola.
- Practice careful hygiene. Avoid contact with blood and body fluids of severely ill people. Do not handle items that may have come in contact with an infected person’s blood or body fluids.
- Avoid funeral or burial rituals that require handling the body of someone who has died from Ebola.
- Avoid contact with animals or with raw meat.
- Avoid hospitals where Ebola patients are being treated. The US Embassy or consulate is often able to provide advice on facilities that are suitable for your needs. The US Embassy in Monrovia can be reached at +(231) 77-677-7000.
- Seek medical care if you develop fever, headache, achiness, sore throat, diarrhea, vomiting, stomach pain, rash, or red eyes.
Special Recommendation for Health Care Workers
- Health care workers who may be exposed to people with the disease should follow these steps:
- Wear protective clothing, including masks, gloves, gowns, and eye protection.
- Practice proper infection control and sterilization measures. For more information, see “Infection Control for Viral Hemorrhagic Fevers in the African Health Care Setting.”
- Isolate Ebola patients from unprotected people.
- Avoid direct contact with the bodies of people who died from Ebola.
- Notify health officials
-
Ebola virus disease
Key facts
- Ebola virus disease (EVD), formerly known as Ebola haemorrhagic fever, is a severe, often fatal illness in humans.
- EVD outbreaks have a case fatality rate of up to 90%.
- EVD outbreaks occur primarily in remote villages in Central and West Africa, near tropical rainforests.
- The virus is transmitted to people from wild animals and spreads in the human population through human-to-human transmission.
- Fruit bats of the Pteropodidae family are considered to be the natural host of the Ebola virus.
- Severely ill patients require intensive supportive care. No licensed specific treatment or vaccine is available for use in people or animals.
Ebola first appeared in 1976 in 2 simultaneous outbreaks, in Nzara, Sudan, and in Yambuku, Democratic Republic of Congo. The latter was in a village situated near the Ebola River, from which the disease takes its name.
Genus Ebolavirus is 1 of 3 members of the Filoviridae family (filovirus), along with genus Marburgvirus and genus Cuevavirus. Genus Ebolavirus comprises 5 distinct species:
- Bundibugyo ebolavirus (BDBV)
- Zaire ebolavirus (EBOV)
- Reston ebolavirus (RESTV)
- Sudan ebolavirus (SUDV)
- Taï Forest ebolavirus (TAFV).
BDBV, EBOV, and SUDV have been associated with large EVD outbreaks in Africa, whereas RESTV and TAFV have not. The RESTV species, found in Philippines and the People’s Republic of China, can infect humans, but no illness or death in humans from this species has been reported to date.
Transmission
Ebola is introduced into the human population through close contact with the blood, secretions, organs or other bodily fluids of infected animals. In Africa, infection has been documented through the handling of infected chimpanzees, gorillas, fruit bats, monkeys, forest antelope and porcupines found ill or dead or in the rainforest.
Ebola then spreads in the community through human-to-human transmission, with infection resulting from direct contact (through broken skin or mucous membranes) with the blood, secretions, organs or other bodily fluids of infected people, and indirect contact with environments contaminated with such fluids. Burial ceremonies in which mourners have direct contact with the body of the deceased person can also play a role in the transmission of Ebola. Men who have recovered from the disease can still transmit the virus through their semen for up to 7 weeks after recovery from illness.
Health-care workers have frequently been infected while treating patients with suspected or confirmed EVD. This has occurred through close contact with patients when infection control precautions are not strictly practiced.
Among workers in contact with monkeys or pigs infected with Reston ebolavirus, several infections have been documented in people who were clinically asymptomatic. Thus, RESTV appears less capable of causing disease in humans than other Ebola species.
However, the only available evidence available comes from healthy adult males. It would be premature to extrapolate the health effects of the virus to all population groups, such as immuno-compromised persons, persons with underlying medical conditions, pregnant women and children. More studies of RESTV are needed before definitive conclusions can be drawn about the pathogenicity and virulence of this virus in humans.
Signs and symptoms
EVD is a severe acute viral illness often characterized by the sudden onset of fever, intense weakness, muscle pain, headache and sore throat. This is followed by vomiting, diarrhoea, rash, impaired kidney and liver function, and in some cases, both internal and external bleeding. Laboratory findings include low white blood cell and platelet counts and elevated liver enzymes.
People are infectious as long as their blood and secretions contain the virus. Ebola virus was isolated from semen 61 days after onset of illness in a man who was infected in a laboratory.
The incubation period, that is, the time interval from infection with the virus to onset of symptoms, is 2 to 21 days.
Diagnosis
Other diseases that should be ruled out before a diagnosis of EVD can be made include: malaria, typhoid fever, shigellosis, cholera, leptospirosis, plague, rickettsiosis, relapsing fever, meningitis, hepatitis and other viral haemorrhagic fevers.
Ebola virus infections can be diagnosed definitively in a laboratory through several types of tests:
- antibody-capture enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)
- antigen detection tests
- serum neutralization test
- reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) assay
- electron microscopy
- virus isolation by cell culture.
Samples from patients are an extreme biohazard risk; testing should be conducted under maximum biological containment conditions.
Vaccine and treatment
No licensed vaccine for EVD is available. Several vaccines are being tested, but none are available for clinical use.
Severely ill patients require intensive supportive care. Patients are frequently dehydrated and require oral rehydration with solutions containing electrolytes or intravenous fluids.
No specific treatment is available. New drug therapies are being evaluated.
Natural host of Ebola virus
In Africa, fruit bats, particularly species of the genera Hypsignathus monstrosus, Epomops franqueti and Myonycteris torquata, are considered possible natural hosts for Ebola virus. As a result, the geographic distribution of Ebolaviruses may overlap with the range of the fruit bats.
Ebola virus in animals
Although non-human primates have been a source of infection for humans, they are not thought to be the reservoir but rather an accidental host like human beings. Since 1994, Ebola outbreaks from the EBOV and TAFV species have been observed in chimpanzees and gorillas.
RESTV has caused severe EVD outbreaks in macaque monkeys (Macaca fascicularis) farmed in Philippines and detected in monkeys imported into the USA in 1989, 1990 and 1996, and in monkeys imported to Italy from Philippines in 1992.
Since 2008, RESTV viruses have been detected during several outbreaks of a deadly disease in pigs in People’s Republic of China and Philippines. Asymptomatic infection in pigs has been reported and experimental inoculations have shown that RESTV cannot cause disease in pigs.
Prevention and control
Controlling Reston ebolavirus in domestic animals
No animal vaccine against RESTV is available. Routine cleaning and disinfection of pig or monkey farms (with sodium hypochlorite or other detergents) should be effective in inactivating the virus.
If an outbreak is suspected, the premises should be quarantined immediately. Culling of infected animals, with close supervision of burial or incineration of carcasses, may be necessary to reduce the risk of animal-to-human transmission. Restricting or banning the movement of animals from infected farms to other areas can reduce the spread of the disease.
As RESTV outbreaks in pigs and monkeys have preceded human infections, the establishment of an active animal health surveillance system to detect new cases is essential in providing early warning for veterinary and human public health authorities.
Reducing the risk of Ebola infection in people
In the absence of effective treatment and a human vaccine, raising awareness of the risk factors for Ebola infection and the protective measures individuals can take is the only way to reduce human infection and death.
In Africa, during EVD outbreaks, educational public health messages for risk reduction should focus on several factors:
- Reducing the risk of wildlife-to-human transmission from contact with infected fruit bats or monkeys/apes and the consumption of their raw meat. Animals should be handled with gloves and other appropriate protective clothing. Animal products (blood and meat) should be thoroughly cooked before consumption.
- Reducing the risk of human-to-human transmission in the community arising from direct or close contact with infected patients, particularly with their bodily fluids. Close physical contact with Ebola patients should be avoided. Gloves and appropriate personal protective equipment should be worn when taking care of ill patients at home. Regular hand washing is required after visiting patients in hospital, as well as after taking care of patients at home.
- Communities affected by Ebola should inform the population about the nature of the disease and about outbreak containment measures, including burial of the dead. People who have died from Ebola should be promptly and safely buried.
Pig farms in Africa can play a role in the amplification of infection because of the presence of fruit bats on these farms. Appropriate biosecurity measures should be in place to limit transmission. For RESTV, educational public health messages should focus on reducing the risk of pig-to-human transmission as a result of unsafe animal husbandry and slaughtering practices, and unsafe consumption of fresh blood, raw milk or animal tissue. Gloves and other appropriate protective clothing should be worn when handling sick animals or their tissues and when slaughtering animals. In regions where RESTV has been reported in pigs, all animal products (blood, meat and milk) should be thoroughly cooked before eating.
Controlling infection in health-care settings
Human-to-human transmission of the Ebola virus is primarily associated with direct or indirect contact with blood and body fluids. Transmission to health-care workers has been reported when appropriate infection control measures have not been observed.
It is not always possible to identify patients with EBV early because initial symptoms may be non-specific. For this reason, it is important that health-care workers apply standard precautions consistently with all patients – regardless of their diagnosis – in all work practices at all times. These include basic hand hygiene, respiratory hygiene, the use of personal protective equipment (according to the risk of splashes or other contact with infected materials), safe injection practices and safe burial practices.
Health-care workers caring for patients with suspected or confirmed Ebola virus should apply, in addition to standard precautions, other infection control measures to avoid any exposure to the patient’s blood and body fluids and direct unprotected contact with the possibly contaminated environment. When in close contact (within 1 metre) of patients with EBV, health-care workers should wear face protection (a face shield or a medical mask and goggles), a clean, non-sterile long-sleeved gown, and gloves (sterile gloves for some procedures).
Laboratory workers are also at risk. Samples taken from suspected human and animal Ebola cases for diagnosis should be handled by trained staff and processed in suitably equipped laboratories.
WHO response
WHO provides expertise and documentation to support disease investigation and control.
Recommendations for infection control while providing care to patients with suspected or confirmed Ebola haemorrhagic fever are provided in: Interim infection control recommendations for care of patients with suspected or confirmed Filovirus (Ebola, Marburg) haemorrhagic fever, March 2008. This document is currently being updated.
WHO has created an aide–memoire on standard precautions in health care (currently being updated). Standard precautions are meant to reduce the risk of transmission of bloodborne and other pathogens. If universally applied, the precautions would help prevent most transmission through exposure to blood and body fluids.
Standard precautions are recommended in the care and treatment of all patients regardless of their perceived or confirmed infectious status. They include the basic level of infection control—hand hygiene, use of personal protective equipment to avoid direct contact with blood and body fluids, prevention of needle stick and injuries from other sharp instruments, and a set of environmental controls.
Table: Chronology of previous Ebola virus disease outbreaks
Year Country Ebolavirus species Cases Deaths Case fatality 2012 Democratic Republic of Congo Bundibugyo 57 29 51% 2012 Uganda Sudan 7 4 57% 2012 Uganda Sudan 24 17 71% 2011 Uganda Sudan 1 1 100% 2008 Democratic Republic of Congo Zaire 32 14 44% 2007 Uganda Bundibugyo 149 37 25% 2007 Democratic Republic of Congo Zaire 264 187 71% 2005 Congo Zaire 12 10 83% 2004 Sudan Sudan 17 7 41% 2003 (Nov-Dec) Congo Zaire 35 29 83% 2003 (Jan-Apr) Congo Zaire 143 128 90% 2001-2002 Congo Zaire 59 44 75% 2001-2002 Gabon Zaire 65 53 82% 2000 Uganda Sudan 425 224 53% 1996 South Africa (ex-Gabon) Zaire 1 1 100% 1996 (Jul-Dec) Gabon Zaire 60 45 75% 1996 (Jan-Apr) Gabon Zaire 31 21 68% 1995 Democratic Republic of Congo Zaire 315 254 81% 1994 Cote d’Ivoire Taï Forest 1 0 0% 1994 Gabon Zaire 52 31 60% 1979 Sudan Sudan 34 22 65% 1977 Democratic Republic of Congo Zaire 1 1 100% 1976 Sudan Sudan 284 151 53% 1976 Democratic Republic of Congo Zaire 318 280 88%
WHO